








To support our efforts please browse our store (books with medicinal info, etc.).
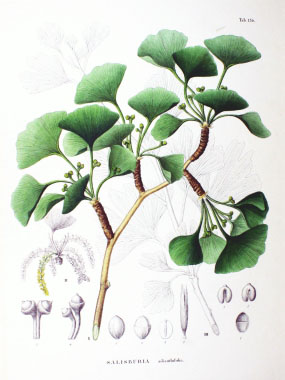
Ginkgo is a tree that is commonly used in landscaping.This tree is of botanical interest because it is the sole survivor of the order Ginkgoales, with fossil evidence tracing back over 200 million years. This tree is the oldest living tree in the world and is referred to as a living fossil. The gingko tree species is native to Southeast Asia, but was brought over to the U.S. in 1784. Even now there are some living Ginkgos in Asia and Japan said to be more than 4,000 years old.
Trunk/Bark
The fissured bark of the gingko is grayish, deeply furrowed on older trees, and has a corky texture. The light-coloured wood, soft and weak. As the tree matures, the bark becomes browner and develops ridges.
Branches/Twigs
Ginkgo branches grow in length by growth of shoots with regularly spaced leaves, as seen on most trees. From the axils of these leaves, "spur shoots" (also known as short shoots) develop on second-year growth. Short shoots have very short internodes (so they may grow only one or two centimeters in several years) and their leaves are usually unlobed.
Height
The gingko grows anywhere from 15 to 24 metres tall and it spreads between 9 and 12 metres.
Leaves/Needles
Fan-shaped ginkgo leaves resemble the leaflets of the maidenhair fern and are borne on short, spurlike but greatly thickened shoots. The leathery leaves are up to 8 cm (3”) long and are sometimes twice as broad. Two parallel veins enter each blade from the point of attachment of the long leafstalk and fork repeatedly toward the leaf edges. Most leaves are divided into two lobes by a central notch.
Flowers
Ginkgos do not reach reproductive age until reaching two-to-four decades of life; at this time, they begin to produce flowers. The trees are dioecious, meaning some trees produce exclusively male flowers while others show only female flowers. When they do bloom, they bloom in April. Male flowers are catkin-like, hanging, and yellow up to 8cm long.
Fruit
The seed measures 1.5 to 2 cm long. Its fleshy outer layer is light yellow-brown, soft, and fruit-like. It is attractive in appearance, but contains butyric acid (also known as butanoic acid) and smells like rancid butter or vomit when fallen.
Habitat
This tree prefers areas in which it can get full sun. It can grow in a variety of soils (sandy, loamy and even clay). If does prefer areas in which there is well-drained soil. It will not grow in the shade. Native to southeastern China, this tree grows in many countries worldwide including parts of the U.S. and Canada.
Edible Parts
The seed is edible; but not the fruit that surrounds it (but only in small amounts). These are a favourite seed used in many ways throughout Asia. The leaves can be used to make a nourishing tea. Leaves aren't harmful if eaten in small quantities, but they are really astringent. The seed and leaves have several medicinal properties. An extract from the leaves is praised by many to help with memory retention.
Other Name
Maidenhair Tree.
Recipes
Winter Survival Food Handbook

PDF Plant Magazines
Types of Wild Food
Geographic Zones Seasons
Disclaimer
EdibleWildFood.com is informational in nature. While we strive to be 100% accurate, it is solely up to the reader to ensure proper plant identification. Some wild plants are poisonous or can have serious adverse health effects.
We are not health professionals, medical doctors, nor are we nutritionists. It is up to the reader to verify nutritional information and health benefits with qualified professionals for all edible plants listed in this web site. Please click here for more information.
Why Edible Wild Food?
- Food costs are rising
- Free, wild food is readily abundant
- Wild food adds nutrition to your diet
- Wild food can help treat various medical conditions





